January 2024
- Patch Tuesday – 1/9
- Windows Server 2012 Officially End Of Support
- CISA Advisory-Excel, Chrome and Sharepoint Vulnerabilities Exploited in the Wild
- Follow Up: 23andMe Alleges Victims Are To Blame For Data Leak
- Citrix Releases January Patch Advisories
- Secret Service Exposes Antivirus Scam in Crackdown
- White House Rolls Out New Regulations On Hospitals Amid Cyber Attacks
- Loan Market Latest Target In String Of Attacks
- SEC Social Media Compromise Leads To Turmoil In Markets
As always, Advanced is proud to be here for all your security needs. Reach out now ([email protected]) to determine how you can improve your security posture and keep your business running!
– The Advanced Security Task Force
| Patch Tuesday – 1/9 |
The 2nd Tuesday of every month is Patch Tuesday! Every Patch Tuesday, Microsoft addresses security vulnerabilities in their products via a large deployment of software updates. This month’s Patch Tuesday addressed 48 security vulnerabilities. The full list can be seen here. This round of updates addressed two critical updates, and to the delight of system administrators everywhere, no Zero-Day Vulnerabilities. Zero-Day Vulnerabilities are publicly disclosed vulnerabilities that had no prior fix available. These often require immediate patching in production environments to mitigate risk.
Of the 48 vulnerabilities addressed, two were regarded as critical. Details on these can be seen below:
- CVE-2024-20700: Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-20674: Windows Kerberos Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
Vulnerabilities of note in this month’s patches include CVE-2024-20677, a remote code execution vulnerability allowing threat actors to insert malicious FBX files into legitimate Office documents. These FBX files, traditionally used for 3D modeling, could then allow the threat actor to run code on the victim’s machine once the document is opened.
As always, end users are advised to practice caution when opening attachments in any email. If you would like to bolster your email security through filtration or end user training, reach out to [email protected].
Advanced deploys patches to all environments as a priority following a testing phase. The criticality of security updates is determined by several factors, primarily the ease of exploitability by threat actors and if the vulnerability has been seen exploited in the wild.
| Windows Server 2012 Officially End Of Support |
- On October 10th, Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 officially reached end of support. This means the operating system will no longer receive critical security patches.
- Windows Server 2012 is considered one of the most popular server operating systems in the world. The retirement is expected to usher in a new wave of threat actors looking to take advantage of deprecated security features.
- Those looking to extend coverage to receive critical patches can subscribe to Extended Security Updates (ESUs). ESUs provide up to 3 years of additional coverage for patches deemed ‘Critical’ and ‘Important’ by Microsoft.
- Servers hosted in Azure are eligible for free ESUs until October 13th, 2026. Servers not hosted in Azure are eligible for ESUs until October 13th, 2026 through purchase of an ESU subscription.
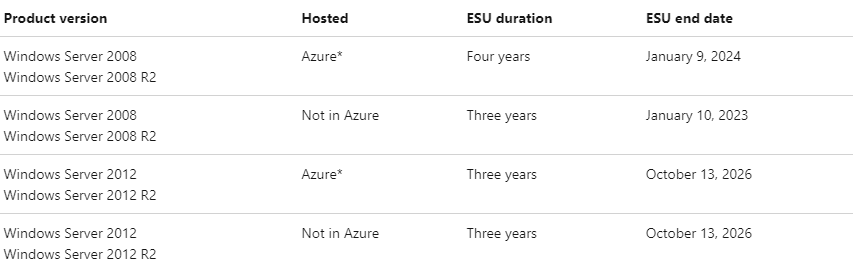
- Advanced recommends clients take immediate action on any out-of-date operating systems. For more information on how these changes can affect your environment, reach out to [email protected].
| CISA Advisory-Excel, Chrome, and Sharepoint Vulnerabilities Exploited in the Wild |
- The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added two vulnerabilities to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog.
- The vulnerabilities include a recently patched flaw in Google Chrome (CVE-2023-7024) and a bug affecting an open-source Perl library for Excel file reading called Spreadsheet::ParseExcel (CVE-2023-7101)
- The security issues have been deemed so severe, Federal agencies have been given until January 23rd to mitigate these security issues according to vendor instructions or to stop using vulnerable products altogether.
- CVE-2023-7101 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Spreadsheet::ParseExcel affecting versions 0.65 and older. When a document with this library passes through a Barracuda Email Security Gateway (ESG), the code runs directly on the ESG through a vulnerability in ‘Amavis’, the local virus scanner native to Barracuda products.
- Barracuda has confirmed several ESGs were targeted by Chinese hackers in late December using this vulnerability to compromise appliances. The threat actor, UNC4841, deployed ‘SeaSpy’ and ‘Saltwater’ malware.
- CVE-2023-7024 is a heap buffer overflow issue in WebRTC in Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge, allowing an attacker to cause crashes or code execution. It was the eighth zero-day vulnerability fixed in Chrome for 2023 and was patched via an emergency update on December 20.
- The vulnerability is exploited when a vulnerable build of Chrome or Edge visits a crafted HTML page. Specifics on the code exploitation are yet to be disclosed to give end users time to patch their browsers.
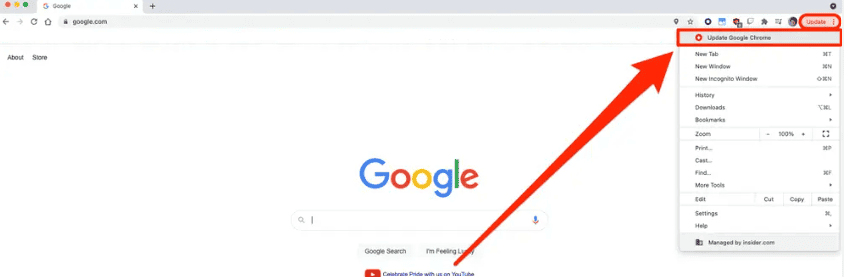
- Advanced automatically deploys browser patches to clients based on agreements. To update Chrome on your mobile devices and personal computers, select the three dots in the upper right hand corner of your screen (shown below).
- CISA has also released an advisory detailing CVE-2023-29357, a remote code vulnerability executed on Microsoft Sharepoint Server.
- Rated 9.8/10 (Critical), the vulnerability would allow a threat actor with a spoofed Java Web Token (JWT) to remotely authenticate as a legitimate user.
- Discovered and patched in June 2023, CISA is now advising all federal systems to ensure systems are patched by January 23rd. It is worth noting that this only affects on-premise deployments of Sharepoint, as opposed to 365/Cloud Based environments. If you have any questions about how this affects your environment, please reach out to [email protected].
| Follow Up: 23andMe Alleges Victims Are To Blame For Data Leak |
- 23andMe, a genetic testing company that offers services in tracing distant relatives, suffered a data breach in October that was originally estimated to have exposed the personal data of roughly 14,000 individuals (.1% of the customer base).
- An additional investigation has confirmed the scope of the breach to be much larger than originally anticipated, with some figures estimating 6.9 million affected individuals in total. The stolen data included the person’s name, birth year, relationship labels, the percentage of DNA shared with relatives, ancestry reports and self-reported location. This estimate shows that roughly half of 23andMe’s 14 million users were affected.
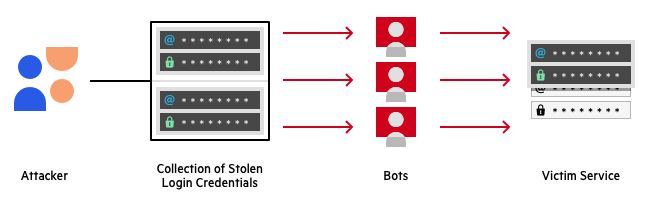
- 23andMe’s internal investigation found that the most likely cause of the breach to be ‘credential stuffing’. Credential stuffing is a common attack in which a threat actor uses a collection of stolen login credentials to attempt to login to various websites. This process is always automated and leverages the likeliness of an end user to repeat usernames and passwords across multiple sites. An overview of this process can be seen below:
- Step 1: A threat actor acquires a list of compromised user accounts and passwords. These are usually captured during data leaks and sold on the dark web or in hacker forums.
- Step 2: A threat actor configures a bot to automatically log into multiple user accounts across various websites.
- Step 3: The threat actor runs an automated process to check if stolen credentials grant access to any web accounts.
- Step 4: The threat actor monitors for successful logins and steals any valuable information.
- Several lawsuits are already in effect against the company, alleging 23andMe changed their terms of service to limit legal exposure following the breach. These changes include a mandatory binding arbitration, which could force users to waive rights to appeal a decision or join a class action lawsuit.
- It is important to note that 23andMe did not have a compromise of any internal systems. The user accounts were accessed legitimately through continued logon attempts. This calls into question if a company is responsible for end users reusing passwords to make accounts easily accessible.
- 23andMe provided plaintiffs with a statement earlier this month, reporting “users negligently recycled and failed to update their passwords following these past security incidents, which are unrelated to 23andMe.”
- This sets an alarming precedent for data security, and should serve as a reminder for all end users to take password security very seriously.
How can we stay safe? You can prevent suffering an account compromise even if your password is leaked through the following methods:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) uses various sign on methods to verify identity. This requires a combination of something you know (like a password) with something you have (like your phone) or something you are (a biometric factor, like your face or a fingerprint).
- Use a Password Manager: Password managers keep all your passwords stored in one place and protects access to that place through MFA. This prevents end users from re-using passwords and ensures passwords are not easily guessable.
- Use Security Questions: Where applicable, you can configure security questions whenever a logon is detected from an unfamiliar device. Make sure your security questions do not contain easily accessible information (such as the high school you attended or your birthday), but instead focus on personal information (like your favorite food or the place of your first date).
| Citrix Releases January Patch Advisories |
- Citrix has released their latest builds for Netscaler Gateway and Citrix Storefront following discovery of three exploited vulnerabilities.
- Administrators have been advised to patch as a priority. Additional details on the vulnerabilities for Citrix Gateway can be seen here. Additional details on Citrix Storefront can be seen here.
- Advanced clients will have these patches addressed automatically. If you have any questions, please reach out any time at [email protected].
| Secret Service Exposes Antivirus Scam in Crackdown |
- A U.S. Secret Service seizure warrant application reveals details on how threat actors stole $34,000 using fake antivirus renewal subscription emails.
- Special Agent Jollif of the United States Secret Service submitted the now-executed seizure warrant to recover funds stolen in a fake Norton subscription renewal email.
- The stolen money was traced to a Chase bank account belonging to “Bingsong Zhou,” associated with phishing scams impersonating Norton Antivirus renewal subscriptions.
- Phishing emails claim the recipient faces charges for renewing an antivirus subscription and instruct them to call a provided number to cancel (shown below).
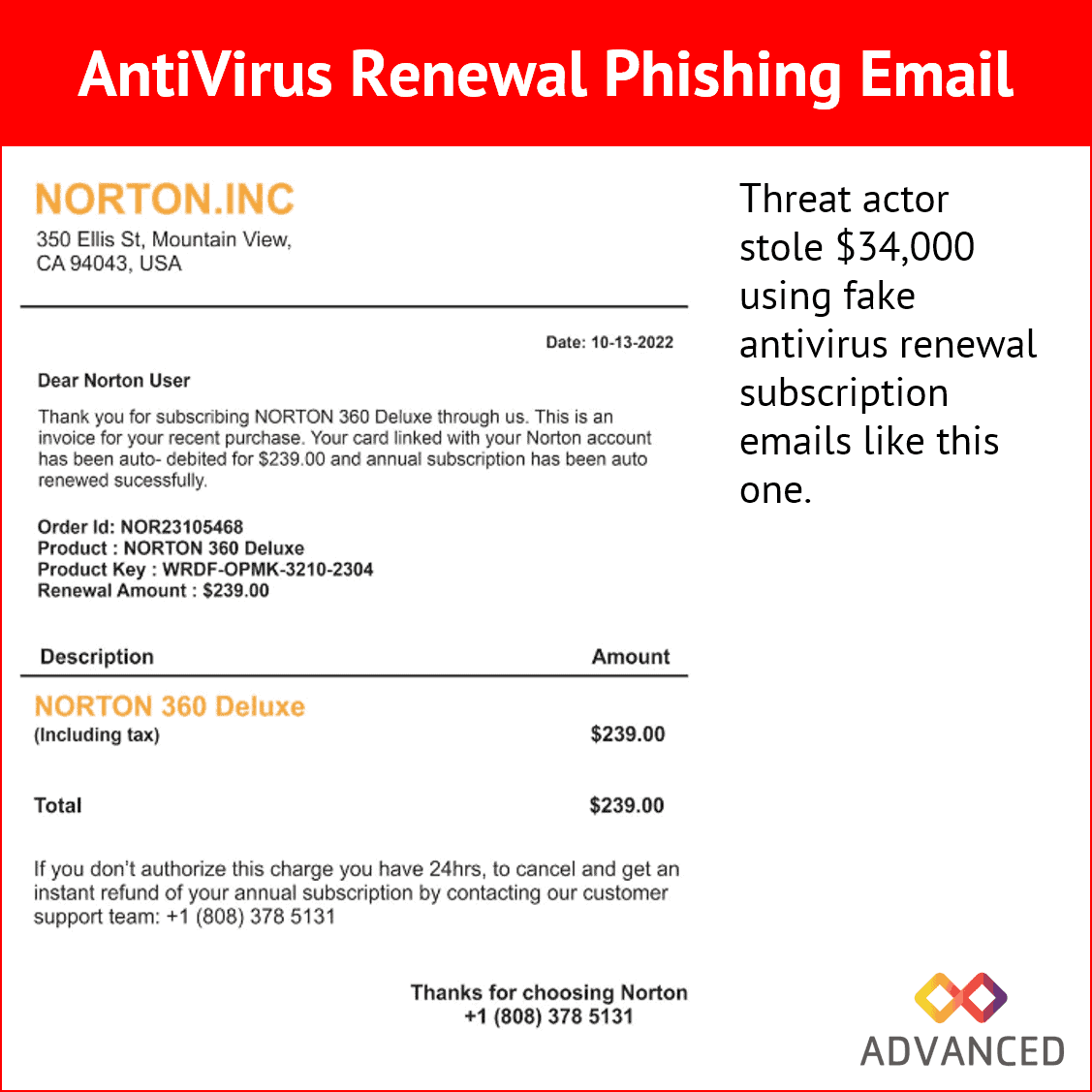
- Victims calling the number are directed by scammers to install remote access software, infect themselves with malware, and enter account credentials on a phishing page.
- The activity, though ongoing for years, has recently increased in volume, according to Special Agent Jollif.
- A highlighted case involves a victim tricked into giving remote access, believing a $34,000 deposit was an error and complying with scammers’ instructions to return the amount.
- Scammers used a blue screen overlay to hide actions, transferring $34,000 from the victim’s Money Market account to their checking balance.
- After identifying the fraud, JP Morgan Chase restricted Zhou’s access to funds, moving them to a suspense account.
- The seizure warrant aims to recover the $34,000 as potentially criminal proceeds, and Zhou faces charges of wire fraud, phishing scam involvement, and potential charges of money laundering, bank fraud, and conspiracy to commit wire fraud.
How Can You Avoid Payment Scams?
- Be on the lookout for any irregular or unexpected invoices for services. If you believe the funds may be legitimate, cross-reference these payments with a trusted party (like your bank) before engaging client support.
- A payment processing error will never require remote access to your personal PC. Do not allow remote access from an unfamiliar party to your personal device under any circumstance.
- Repayment scams are becoming increasingly common. If a company ever advises you that funds have been paid to you in error and need to be refunded, end the call and engage your bank immediately. Threat actors with remote access to your PC will display fake images and overlays to deceive you into “paying back” your own money.
| White House Rolls Out New Regulations On Hospitals Amid Cyber Attacks |
- The Biden administration plans to introduce new cybersecurity requirements for hospitals to address the increasing frequency of cyberattacks targeting healthcare providers.
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will propose rules within the next month, making it mandatory for hospitals to establish basic digital security defenses to qualify for federal funding.
- The government aims to focus on key cybersecurity practices that have a meaningful impact, with the new requirements expected to take effect before the end of the year.
- Hospitals, heavily reliant on technology, have been frequent targets of cybercriminals, leading to disruptions in medical procedures and concerns about patient safety.
- The cyber rules will become part of the existing requirements governing hospital operations, including building design and patient interactions, for reimbursement from Medicare and Medicaid programs.
- The proposed cybersecurity requirements include implementing multi-factor authentication and operating a program to promptly fix software vulnerabilities upon discovery.
- The Biden administration has taken a more proactive stance on cybersecurity, using existing authorities to enact requirements for critical industries, following the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in May 2021.
New regulations include:
- Publish voluntary Health care and Public Health sector Cybersecurity Performance Goals (HPH CPGs). HHS will release HPH CPGs to help health care institutions plan and prioritize implementation of high-impact cybersecurity practices.
- Provide resources to incentivize and implement cybersecurity practices. HHS will work with Congress to obtain new authority and funding to administer financial support and incentives for domestic hospitals to implement high-impact cybersecurity practices.
- Implement an HHS-wide strategy to support greater enforcement and accountability. HHS will propose new enforceable cybersecurity standards, informed by the HPH CPGs, that would be incorporated into existing programs, including Medicare and Medicaid and the HIPAA Security Rule.
- Expand and mature the one-stop shop within HHS for healthcare sector cybersecurity. HHS will mature the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response’s (ASPR) coordination role as a “one-stop shop” for health care cybersecurity which will improve coordination within HHS and the Federal Government, deepen HHS and the Federal government’s partnership with industry, improve access and uptake of government support and services, and increase HHS’s incident response capabilities.
| Loan Market Latest Target In String Of Attacks |
-
- LoanDepot, a major U.S. nonbank mortgage lender, confirmed a ransomware attack in a recent 8-K filing with the SEC. At this time, no group has claimed responsibility for the attack.
- Customers faced issues accessing the payment portal on last week, prompting LoanDepot to take certain systems offline and work on restoring normal operations.
- The company is actively investigating the extent of the incident with external cybersecurity experts, notifying regulators, and collaborating with law enforcement agencies.
- Recurring automatic payments will be processed but may experience delays in appearing in payment history; new payments through the servicing portal are temporarily unavailable.
- Some systems were shut down to prevent attackers from accessing other devices on the network; the company continues to assess the incident’s impact.
- The breach follows a similar incident in May 2023 when LoanDepot disclosed a data breach resulting from a cyberattack in August 2022, exposing customer data.
- Other mortgage lenders, such as Mr. Cooper, also experienced cyberattacks and data breaches in November 2023, affecting millions of customers.
- The incident highlights the ongoing cybersecurity challenges faced by financial institutions, emphasizing the need for vigilance and enhanced security measures.
| SEC Social Media Compromise Leads To Turmoil In Markets |
- @SECGov, the X/Twitter account handle for the US Securities and Exchange Commission, was compromised
- X’s safety team reported the SEC did not have two-factor authentication (2FA) enabled on its main X account, leading to a security breach.
- While MFA was not enforced, the hack occurred through a SIM swap, where an unidentified actor gained control of the phone number associated with the @SECGov account and accessed it through a third party.
- A SIM swap hack involves identity theft, allowing attackers to take over a victim’s phone number and access various accounts, including social media, banks, and cryptocurrencies.
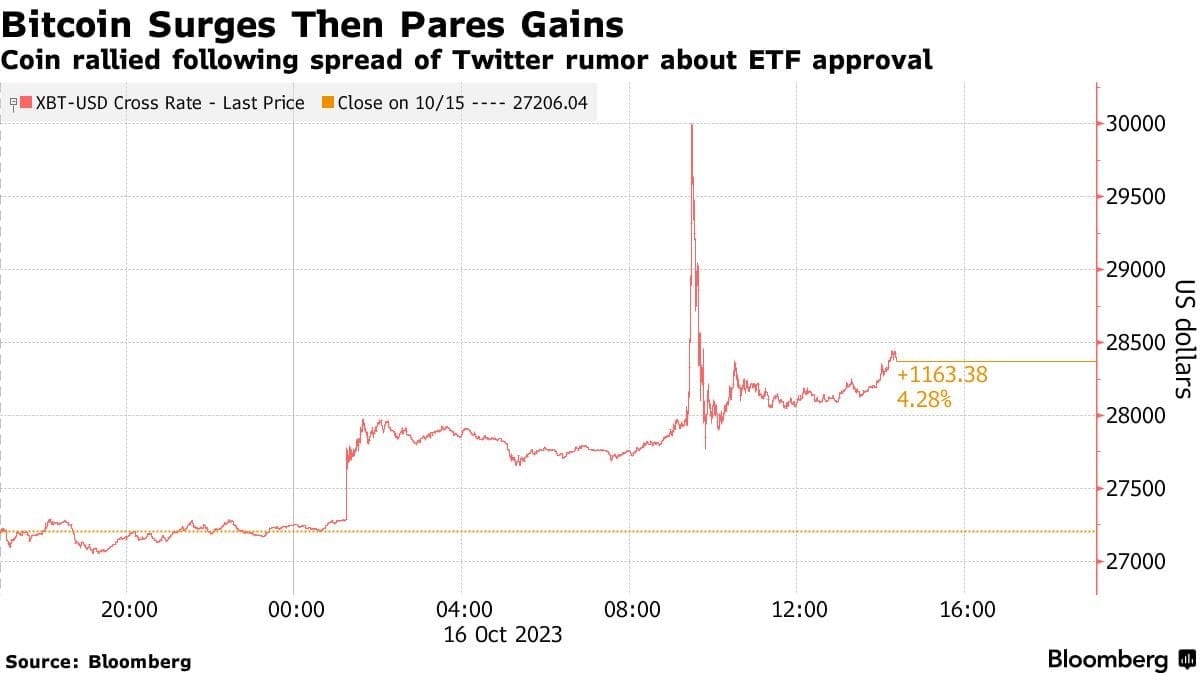
- While compromised, the threat actor sent a Tweet reporting that Bitcoin had been approved for a U.S backed Exchange Traded Fund (or ETF), causing volatility in the cryptocurrency market.
- The incident underscores concern about cybersecurity procedures and accountability within regulatory agencies, particularly in the context of market-moving mistakes.
Advanced recommends taking the following steps to ensure you are protected in the event of a compromise:
- Ensure MFA is enabled for every cloud-based account you have.
- Ensure a recovery email, besides your standard email, is in place on all cloud-based accounts. This email should also be protected by MFA.
- Ensure account monitoring and notifications are enabled to alert you to new sign on attempts and new numbers added to your accounts.
Sources:
- January 2024 Security Updates
- 23andMe tells victims it’s their fault that their data was breached
- LoanDepot Takes Systems Offline Following Ransomware Attack
- CISA Urges Patching of Exploited SharePoint Server Vulnerability
- HHS Announces Next Steps in Ongoing Work to Enhance Cybersecurity for Health Care and Public Health Sectors
- US court docs expose fake antivirus renewal phishing tactics
- SEC did not have 2FA enabled: X safety team on fake Bitcoin ETF post